Antibody to reduce brain inflammation and atrophy in sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE)
減少大腦炎症和萎縮的抗體 膿毒症相關腦病 (SAE)

CA mAb suppresses microglia and astrocyte activation and brain atrophy in LPS-induced systemic sepsis model.
CA mAb modulates microglia/macrophages polarization toward M2-like (anti-inflammation, repairing) and reduces M1-like (pro-inflammation, damaging) to suppress inflammation.
CA mAb 在 LPS 誘導的全身性敗血症模型中抑制小膠質細胞和星形膠質細胞活化以及腦萎縮。
CA mAb 調節小膠質細胞/巨噬細胞向 M2 樣極化(抗炎、修復)並減少 M1 樣(促炎、破壞)以抑制炎症。
 Targeted indication
Targeted indication
Suppress brain inflammation and atrophy in systemic sepsis-induced brain inflammation (IP injection).
 Status
Status
Monoclonal Abs available; Animal mouse models
 Key features
Key features
- Effective therapeutic drugs are required to suppress brain inflammation and atrophy in SAE.
- A simple and efficient method to modulate macrophage/microglia polarization from M1 to M2.
- Much less mAb required (1/10 to 1/30 of regular dose). Safe, less ADCC
 Market
Market
Therapy for inflammatory related brain and systemic diseases, including psoriasis, and brain and other systemic inflammatory related diseases.
Market for Ab drugs to inhibit inflammation: more than US$40 billion/year.
No effective therapeutic agents are available to suppress brain inflammation, such as in stroke, brain trauma and sepsis-induced brain encephalopathy (SAE).
Modulation of macrophage polarization from pro-inflammatory (M1-like) toward anti-inflammatory (M2-like) phenotypes to curb inflammation has CA mAbs reduce brain inflammation CA mAbs reduce brain atrophy become an important approach clinically, including brain diseases, while the effect remains unsatisfactory.
CA mAb modified macrophages will migrate into brain and tissues to suppress local inflammation which circumvent the drawback of Ab drugs that cannot get through the blood brain barrier.
Much less Ab required may reduce side effects such as ADCC.
MODE OF ACTION

EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
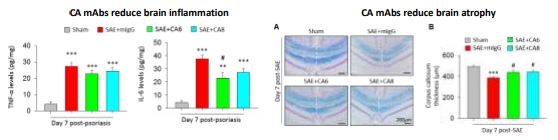
CA mAbs attenuated TNF-α and IL-6 expression in bone marrow-derived macrophages post-LPS induction.
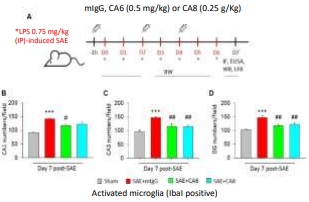
IP injection of CA mAb (0.25 – 0.5 mg/kg) reduces microglia and astrocyte activation, brain atrophy and TNF-α and IL-6 expression in LPS-induced SAE mouse model.
Much less mAb required (0.25 – 0.5 mg/kg, compared with 10 to 30 mg/kg in other mouse studies), expecting to have less ADCC (Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity)
Ab will not bind to non-immune cells: less side-effects.
Four CA mAbs constructed and sequenced. Two of them have been tested with anti-inflammatory efficacy
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY
Licensing and/or Collaboration, Sponsored Research
CONTACT
service@biip-dcc.org
